# 此页面贡献者:小钻风
算法:非递归遍历二叉树
实现非递归遍历二叉树的原理就是使用栈来模拟递归的情况。
假设有如下二叉树:
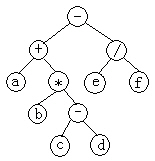
期望:
广度优先遍历的序列:-+/a*efb-cd
深度优先遍历:
- 先序遍历的序列是:-+a*b-cd/ef
- 中序遍历的序列是:a+b*c-d-e/f
- 后序遍历的序列是:abcd-*+ef/-
对象形式:
const tree = {
value: '-',
left: {
value: '+',
left: {
value: 'a'
},
right: {
value: '*',
left: {
value: 'b'
},
right: {
value: '-',
left: {
value: 'c'
},
right: {
value: 'd'
}
}
}
},
right: {
value: '/',
left: {
value: 'e'
},
right: {
value: 'f'
}
}
}
广度优先遍历
const breadthFirstTraversal = function (node) {
if (node) {
const stack = []
stack.push(node)
while (stack.length !== 0) {
node = stack.shift()
console.log(node.value)
if (node.left) stack.push(node.left)
if (node.right) stack.push(node.right)
}
}
}
深度优先遍历
先序遍历
const preOrderTraversal = function (node) {
if (node) {
const stack = []
stack.push(node)
while(stack.length !== 0) {
node = stack.pop()
console.log(node.value)
if(node.right) stack.push(node.right)
if(node.left) stack.push(node.left)
}
}
}
中序遍历
const inOrderTraversal = function (node) {
if (node) {
const stack = []
while (stack.length !== 0 || node) {
if (node) {
stack.push(node)
node = node.left
} else {
node = stack.pop()
console.log(node.value)
node = node.right
}
}
}
}
后序遍历
const postOrderTraversal= function (node) {
if(node) {
const stack = []
stack.push(node)
let temp = null
while (stack.length !== 0) {
temp = stack[stack.length - 1]
if (temp.left && node !== temp.left && node !== temp.right) {
stack.push(temp.left)
} else if (temp.right && node !== temp.right) {
stack.push(temp.right)
} else {
console.log(stack.pop().value)
node = temp
}
}
}
}